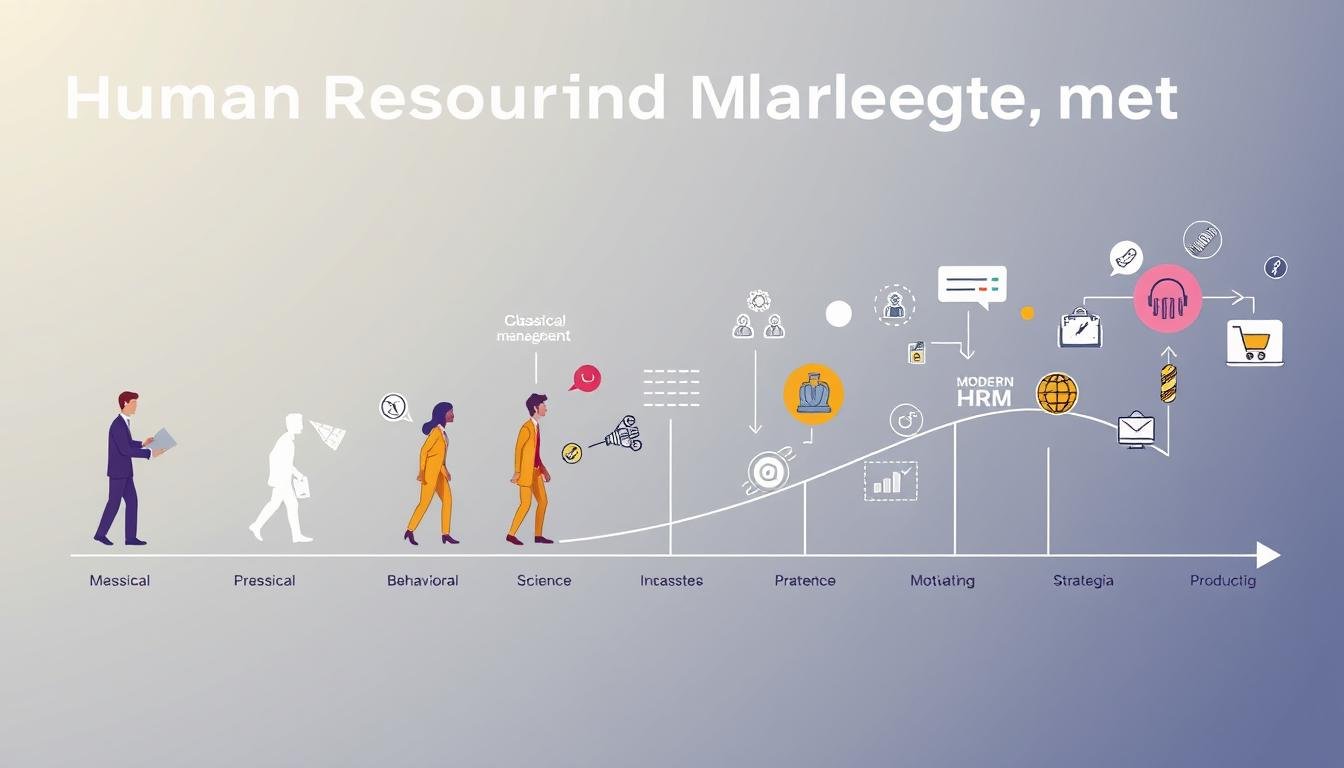
Exploring the Evolution of Human Resource Management Theories
The story of Human Resource Management (HRM) is truly captivating. It spans from ancient times to the present day. This journey shows how our views on managing people and organizations have changed.
In ancient places like Mesopotamia, Egypt, and China, the basics of managing workers began. These early steps grew through the Middle Ages, with guilds in Europe handling apprenticeships and work rules. The Industrial Revolution then brought a big change, making HR roles official and creating personnel departments.
In the early 1900s, personnel management started to take shape. It focused on keeping records and following rules. After World War II, the Human Relations Movement came along, focusing on the mental side of work. By the 1960s and 1970s, HRM became a key part of business, linking people with company goals.
Now, strategic HRM leads the way. It uses technology to manage data and track performance well. This shows we understand more about people and how they help businesses succeed.
Key Takeaways
- HRM roots trace back to ancient civilizations
- Industrial Revolution formalized HR functions
- Human Relations Movement emphasized psychological factors
- Personnel management evolved into strategic HRM
- Technology plays a crucial role in modern HRM practices
- HRM now focuses on aligning human capital with business objectives
Introduction to Human Resource Management Theories
Human Resource Management (HRM) theories are key to good Workforce Planning Strategies. They have changed over time, guiding how companies manage their teams. Let’s look at why these theories matter and where they come from.
Importance of HRM Theories
HRM theories help us understand and manage people in the workplace. They help companies plan their workforce and manage talent. These theories aid HR experts in making better choices, boosting employee performance, and aligning HR with business goals.
Historical Context of HRM
HRM theories started long ago, but really took off during the Industrial Revolution. In the early 1980s, universities in the U.S., Britain, and Canada started teaching HRM. The 1990s saw HRM become a fast-growing field in Europe.
Important theories in HRM include:
- Organizational Lifecycle Theory
- Strategic Contingency Theory
- General Systems Theory
- Transaction Cost Theory
These theories have shaped how companies plan their workforce and manage talent. They focus on motivating employees, leadership, and how organizations work. For example, Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and Frederick Herzberg’s Motivation-Hygiene Theory have greatly influenced employee motivation and job satisfaction.
“HR theories aim to increase job performance efficiency and worker motivation or commitment.”
As HRM keeps growing, new theories appear to tackle today’s workplace issues. These new ideas will shape the future of Workforce Planning Strategies and Talent Management Approaches.
The Classical Management Theories
The Classical Management Theories set the stage for today’s Human Resource Management. They came up during the Industrial Revolution. This was a time when workers moved from family businesses to factories, leading to big productivity gains.
This change showed the need for better organization and efficiency in the workplace.
Scientific Management
Frederick W. Taylor’s Scientific Management theory is still important today. It focuses on making tasks more efficient. Taylor suggested studying tasks, matching workers to jobs, monitoring closely, and training employees.
He aimed to standardize processes to increase productivity. He analyzed task times and motions to find the most efficient ways to do things.
Administrative Theory
Henri Fayol’s Administrative Theory outlined six management functions and 14 principles. It stresses the importance of managerial efficiency in supervising and training teams. Managers should plan, organize employees based on skills, resolve conflicts, communicate well, and align with company goals.
Bureaucratic Management
Max Weber’s Bureaucratic Theory proposed a hierarchical structure with clear rules. It suggests that all employees in large organizations should have specific titles showing their authority and responsibility. This approach aims to achieve equality and rationality in organizational structures.
While these theories bring benefits like streamlined operations and increased productivity, they sometimes overlook employees’ social needs and creativity. Modern Employee Engagement Models often blend these classical principles with today’s workforce needs. They focus on well-being and adaptability for lasting success.
The Human Relations Movement
The Human Relations Movement changed how we think about management. It started with the Hawthorne studies by Elton Mayo and Fritz Roethlisberger from 1924 to 1932. They found that work’s psychological and social sides are key to success.
Key Figures in the Movement
Elton Mayo is known as the Human Relations Movement’s founder. His Hawthorne studies showed how social and job satisfaction affect work. Abraham Maslow and Douglas McGregor also added important ideas, focusing on personal drive and positive management.
Principles of Human Relations
The Human Relations Movement’s main ideas are:
- Seeing the value of social interactions at work
- Putting employee happiness and motivation first
- Understanding the power of group and informal work bonds
- Seeing work as a natural part of life
- Empowering workers and sharing the company’s vision
Impact on HRM Practices
The Human Relations Movement changed HRM a lot. It made HR focus more on supporting workers, improving communication, and having positive leaders. Now, HR cares more about worker happiness, motivation, and how they get along.
This change led to better training, team activities, and rewards for both individual and team efforts. It’s made HRM more about people and less about just numbers.
Bringing human relations ideas to life can be tough in big companies. Yet, many have seen success by making employee management more personal. This human focus keeps shaping today’s HRM, guiding how companies manage talent and build their work culture.
Behavioral Theories in HRM
Behavioral theories in Human Resource Management (HRM) have greatly influenced Human Capital Development and Employee Engagement Models. These theories give insights into what motivates and satisfies employees. They help shape how organizations design jobs and work environments.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Abraham Maslow’s theory says human needs follow a hierarchy. This idea is key for employee motivation strategies. By meeting different levels of needs, from basic to self-actualization, organizations can boost job satisfaction.
Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
Frederick Herzberg’s theory separates motivators from hygiene factors. Motivators, like recognition and growth, increase job satisfaction. Hygiene factors, like salary and work conditions, prevent dissatisfaction but don’t motivate.
Implications for Employee Motivation
These theories have shaped modern Employee Engagement Models. By knowing what motivates each employee, organizations can create strategies to improve productivity and job satisfaction. This approach fits with the behavior perspective in strategic HRM, focusing on matching practices with employee preferences.
| Theory | Key Concept | Application in HRM |
|---|---|---|
| Maslow’s Hierarchy | Five levels of needs | Addressing various employee needs |
| Herzberg’s Two-Factor | Motivators vs. Hygiene factors | Designing motivating job roles |
By using these behavioral theories, organizations can unlock their human resources’ full potential. This gives them a competitive edge in today’s fast-changing business world. It leads to a positive work environment, driving success through better employee engagement and performance.
Systematic Theories of HRM
Systematic theories of HRM see organizations as connected systems. They stress the need to match HR plans with business goals. Let’s look at some key systematic theories that guide modern Organizational Behavior Principles and Workforce Planning Strategies.
Overview of System Theories
Four main theories lead the systematic approach to HRM:
- Organizational Lifecycle Theory
- Strategic Contingency Theory
- General Systems Theory
- Transaction Cost Theory
Each theory gives a different view on managing human resources. The Organizational Lifecycle Theory sees organizations as living beings, growing and then declining. Strategic Contingency Theory focuses on leadership in solving complex HR problems.
Relationships Between HR and Organizational Systems
General Systems Theory sees organizations as parts connected by the environment. Changes in one part affect the whole. This view is key for good Workforce Planning Strategies. Transaction Cost Theory looks at the costs of outsourcing, showing the value of doing some HR tasks in-house.
| Theory | Key Focus | Impact on HR Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Organizational Lifecycle | Stages of organizational growth | Adapting HR strategies to organizational stage |
| Strategic Contingency | Leadership in problem-solving | Developing leadership for HR challenges |
| General Systems | Interconnectedness of organizational parts | Holistic approach to HR management |
| Transaction Cost | Costs of outsourcing vs. internalizing | Optimizing HR function allocation |
Knowing these systematic theories helps HR pros make better Workforce Planning Strategies. By seeing HR through these theories, companies can manage their human resources more effectively and in a more integrated way.
The Contingency Approach to HRM
The contingency approach to Human Resource Management (HRM) believes that there’s no single way to manage people. It’s a flexible method that adjusts to each organization’s needs. It looks at things like company size, industry, and culture.
What is the Contingency Theory?
Contingency theory in HRM says that HR practices work best when they match the situation. It tells HR pros to make strategies that fit their organization’s unique needs.
- Fiedler’s Contingency Theory: Focuses on leadership effectiveness based on situational factors
- Situational Leadership Theory: Identifies four leadership styles suited to different employee competence levels
- Path-Goal Theory: Emphasizes leader behavior adaptations for motivating followers
Variables Affecting HR Decisions
Several factors shape HR decisions in the contingency approach:
| Variable | Impact on HR Decisions |
|---|---|
| Organizational Structure | Determines communication channels and decision-making processes |
| Technology | Influences job design and skill requirements |
| Competitive Strategy | Shapes talent acquisition and development priorities |
| Labor Market Conditions | Affects recruitment strategies and compensation policies |
HR Analytics and Metrics are key in the contingency approach. They offer insights for making decisions that fit the organization. By using these tools, companies can improve how they manage talent. This leads to better employee engagement and performance.
The Rise of Strategic Human Resource Management
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) is a big change in HR practices. It links workforce strategies with company goals. It sees Human Capital Development as key to success.
Defining Strategic HRM
SHRM started in the late 20th century. It sees employees as strategic assets. Wright & McMahan (1992) said it’s “the pattern of planned human resource deployments and activities intended to enable an organization to achieve its goals.” This changed HR from just admin work to a strategic role.
Aligning HR Strategy with Business Goals
SHRM aims to link HR practices with company goals. This means:
- Long-term Workforce Planning Strategies
- Measuring HR’s impact on performance
- Developing HR systems that support business strategies
Research shows SHRM is linked to business success. Studies by Huselid (1995) and MacDuffie (1995) found strong links between SHRM and financial performance, employee productivity, and customer alignment.
| SHRM Focus Areas | Impact on Business |
|---|---|
| Employee Development | Improved skill sets, increased productivity |
| Performance Management | Better alignment with organizational goals |
| Talent Acquisition | Enhanced workforce quality and fit |
| Compensation Strategies | Increased employee motivation and retention |
By using SHRM, companies can get ahead through their workforce. This leads to innovation and adaptability in today’s fast-changing business world.
The Role of Technology in HRM Evolution
Technology has changed Human Resource Management (HRM) a lot. It has made old ways of doing things more efficient and based on data. This change has brought up HR Analytics and Metrics, changing how companies manage their workers and keep them engaged.
Automation and HR Software
Automation in HRM has made things much better. Things like the Internet-of-Things, Big Data, and Artificial Intelligence have made HRM processes smoother. This has made HR teams work better and has helped employees get better at their jobs.
Data Analytics in HR Decision-Making
HR Analytics and Metrics are key in today’s HRM. They help companies make smart choices about their workforce. For example, looking at data on who works there and how they feel helps spot unfairness in HR rules. This way, HR can take on bigger roles in the company.
| Technology | Impact on HRM |
|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence | Automates processes, improves efficiency |
| Cloud Computing | Enhances accessibility of HR information systems |
| Internet of Things | Facilitates real-time data collection and analysis |
The growth of HRM roles shows how important digital HRM technology is. It helps make decisions based on data and strategic planning. This technology has not only made things run smoother but has also helped with communication and made HR professionals more effective.
Contemporary HRM Theories
The field of Human Resource Management (HRM) has grown a lot since the 1980s. Today, HR focuses on new workplace trends and changes in society. Let’s look at some important HRM theories now.
Diversity and Inclusion
Workplace Diversity and Inclusion is now a big deal in HRM. Companies see the importance of welcoming everyone, no matter their race, gender, age, or background. This approach leads to more innovation, happier employees, and better retention.
Employee Engagement Frameworks
HR uses employee engagement frameworks to increase productivity and loyalty. These include regular feedback, personal development plans, and recognition programs. The goal is to make employees more motivated and loyal.
Sustainability in HRM
Sustainability is now a big part of HRM. It’s not just about the environment but also about long-term planning, ethics, and giving back to society. Sustainable HRM aims to meet business needs while caring for employees and society.
| Contemporary HRM Focus | Key Objectives |
|---|---|
| Diversity and Inclusion | Create inclusive environments, foster innovation |
| Employee Engagement | Boost productivity, improve retention |
| Sustainability | Balance business needs with employee and societal well-being |
These modern theories show how HRM keeps evolving. As workplaces change, HR must keep up. Change Management in HR is key to successfully adopting these new strategies. This ensures companies can succeed in a constantly changing world.
Globalization and HRM Theories
The global job market now has about 3.4 billion people. This change has made HR professionals adjust their strategies to fit an interconnected world. With globalization, businesses can work in over 140 countries, making hiring easier and finding diverse talent.
Challenges of Global HRM
Global HRM has its own challenges like legal issues, keeping talent, and coordinating communication. Hiring from certain countries can save money and offer tax perks. But, it also makes managing the workforce harder.
HR experts must deal with cultural differences, language issues, and different laws. This ensures operations run smoothly.
Cross-Cultural Management Theories
Cross-cultural management theories help HR manage global teams well. These theories stress the need for cultural understanding and flexibility in leadership. By valuing cultural differences, HR can boost innovation and growth.
In a global setting, talent management needs to be flexible and creative. Employer of Record (EOR) services help manage global teams, ensuring legal and payroll issues are handled. This lets HR focus on important tasks like planning for the future and promoting diversity.
| Global HRM Benefits | Global HRM Challenges |
|---|---|
| Access to diverse talent | Cultural misunderstandings |
| Market expansion opportunities | Legal compliance complexities |
| Reduced labor costs | Communication barriers |
| Increased innovation potential | Talent retention difficulties |
Future Trends in Human Resource Management
The world of Human Resource Management is changing fast. New technologies and shifts in the workforce are leading the way. HR experts are facing new challenges and finding new opportunities in the future of work.
The Impact of Remote Work
Remote work has changed HR forever. A big 40% of workers might leave if they can’t work from home. This means HR needs new ways to manage teams and keep employees engaged.
Emerging HR Technologies
HR is leading in tech innovation. AI is making tasks like finding talent and onboarding easier. Chatbots help manage talent and improve work performance. These tools are making HR work more efficient and based on data.
Evolving Employee Expectations
Today’s workers want more than just a salary. They want balance, learning, and meaningful work. HR is focusing on well-being, diversity, and skills to meet these needs. This helps keep the best employees happy and engaged.
| Future HR Trends | Impact |
|---|---|
| Remote-first strategies | Increased flexibility, global talent access |
| AI in HR | Enhanced efficiency, data-driven decisions |
| Employee well-being focus | Improved retention, higher engagement |
Conclusion: The Continual Evolution of HRM Theories
Exploring the Evolution of Human Resource Management Theories is truly fascinating. It has evolved from the 18th century to today’s digital age. HRM has grown from simple record-keeping to a strategic partner in business success.
Summary of Key Theories
HR Theories History shows a shift from focusing on tasks to valuing people. The early 1900s saw the scientific management era. By the 1980s, HRM became a key part of business strategy.
Today, it covers hiring, training, and shaping company culture. This shows how much HRM has evolved.
The Path Ahead for HRM Practices
Looking ahead, HRM will keep changing with the times. Digital tools and data analysis are already shaping how companies manage their workforce. The focus on employee well-being and diversity is growing stronger.
As work becomes more global and flexible, HRM will need to adapt. The future of HRM lies in balancing technology with the human touch. This ensures that people remain at the heart of every organization.
Source Links
- Exploring the Evolution: A Brief History of HRM
- IJECM
- What are HR Theories? Types and Meaning
- Human resource management theories
- A Guide to Popular Management Theories
- Classical Management Theory: How Does It Work?
- Basics of Human Relations Management Theory
- How the Human Relations Movement Changed Management
- What is Human Relations Theory? A Complete Guide – TheMBAins
- No Best Way: An Evolutionary Perspective on Human Resource Management
- Different Management Theories | Organizational Behavior and Human Relations
- What is the history of Human Resource Management(HRM)?
- Contingency Approach
- The Contingency Approach In Management: Definition, Characteristics & Benefits
- A Road Well Traveled: The Past, Present, and Future Journey of Strategic Human Resource Management
- Strategic human resource management: The evolution of the field
- JIDT
- Human Resource Technology and the Changing Role of Human Resource Professionals
- The Evolution of Human Resource Management (HRM)
- 8 HR Models Every HR Practitioner Should Know in 2025
- Impact of Globalization in Human Resource (HR) Management
- Exploring Human Resource Management Digital Transformation in the Digital Age
- The Evolution of Human Resource Management (HRM)
- 7 Emerging Trends in Human Resource Management (HRM)
- The Evolution of HRM: Understanding its Features, Objectives, and Characteristics
- Evolution of Personnel and HR: A Historical Overview
- The Evolution of HRM (Human Resource Management)